Retaining Ring FAQ's
-1.png)
What are retaining rings and where are they used?
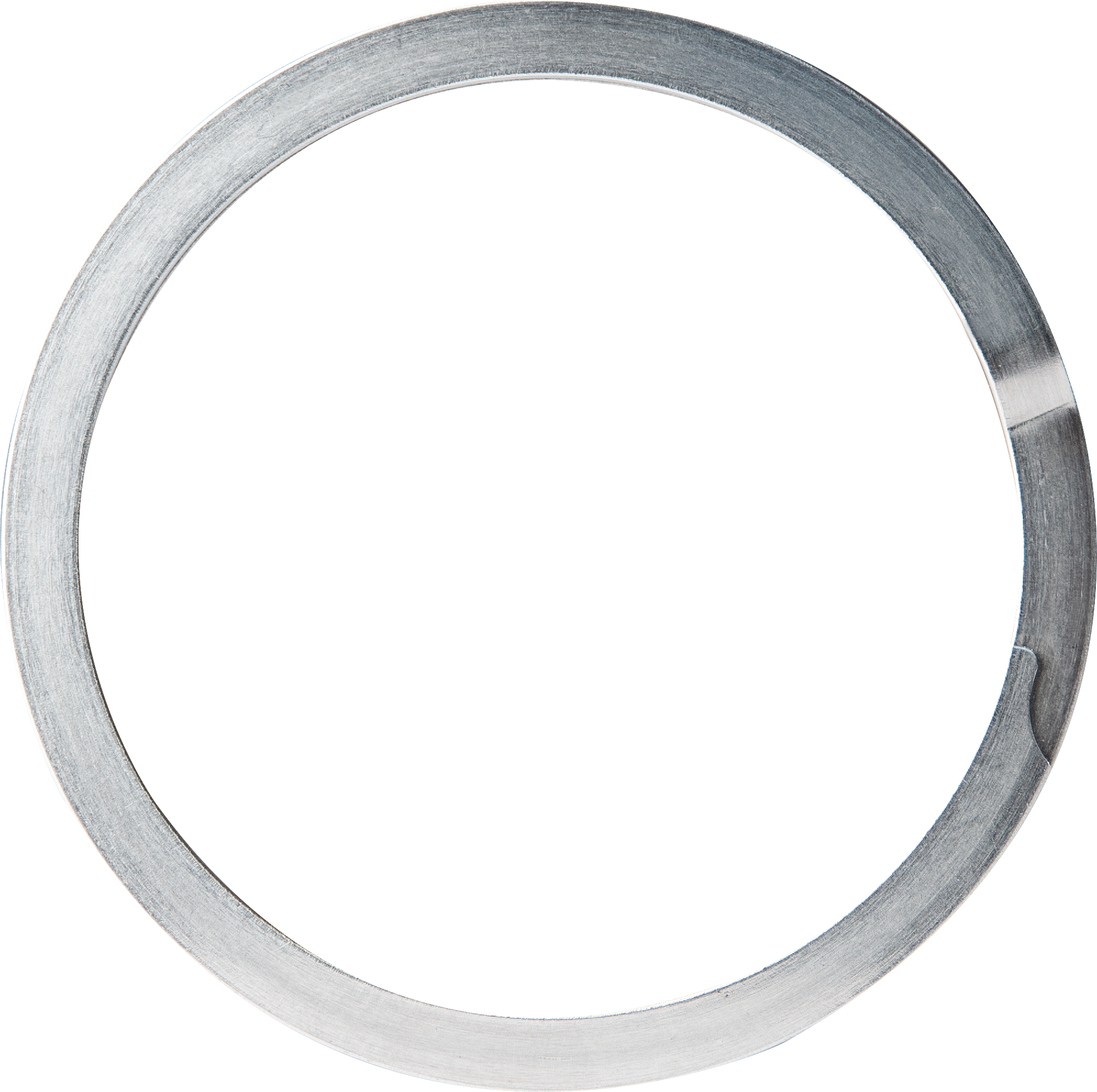
Retaining rings—also known as snap rings and circlips—are metal fasteners installed into a groove on a shaft or in a housing or bore to retain an assembly. They keep parts in place using a compact, lightweight design that requires fewer machining operations than other fastening techniques.
Engineers specify retaining rings based on their installation and removal needs, rotational speed of the application, expected force loads on the ring, the conditions of the operating environment, and cost.
They can range in size from 1mm to 1m in diameter, and work in a wide variety of industries and applications.
What retaining ring styles are available?
Retaining rings can be sorted into three main categories by their design attributes. Tapered and constant section retaining rings are a nearly complete circle with a gap between two free ends.
Tapered-section rings decrease in width from the top of the ring to the free ends. Installed, they make continuous contact within their installation groove. Some tapered-section rings designed for axial installation feature lugs that make them easier to expand and place.
Constant section rings, in contrast, have the same width throughout their circumference. The resulting stiffer cross section results in contact at three points within the installation groove and typically do not have lugs.
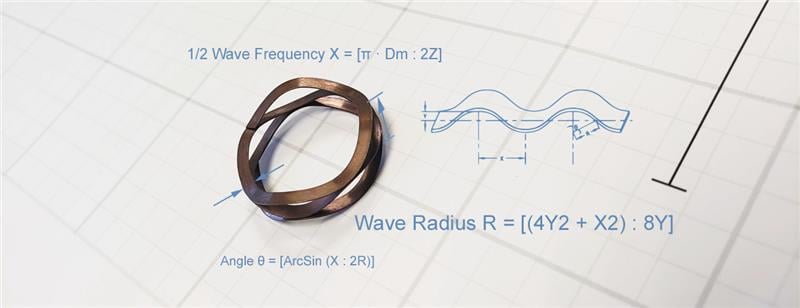
Spiral rings are made from flat wire coiled two or three times around the circumference. They make 360° contact within their groove and have a constant width around their circumference. Spiral rings are not usually designed with installation lugs. Instead, they may have notched ends that aid in their removal.
Which retaining rings can handle the speeds and forces of my application?
When choosing a retaining ring, you should take the demands of your application into account. Some styles of tapered section rings have significant radial spring force that can handle high RPM applications and high loads. However, some radially installed tapered-section rings are not suited to high speeds or forces, so be sure to check each style’s ratings.
Spiral rings work well with high loads, especially in applications where resilience to dynamic loading is needed. They are generally considered to have lower RPM capabilities than tapered section rings. They are well balanced and available in materials and styles ranging from light duty to heavy duty based on the force load you need to retain.
Though constant-section rings are typically used in applications with lower load and speed requirements, don’t overlook them. Several constant-section styles are available that can bear significant loads at an attractive price point.
Which rings meet my installation and removal requirements?
Consider your preferred installation method and the frequency with which you’ll be installing and removing the rings. For instance, the lugs on axially installed tapered-section retaining rings make them easy to install and uninstall with commonly available tools like retaining ring pliers. Keep in mind, designers must ensure they leave clearance for the lugs and room for the pliers to fit within the design.
Constant-section rings are manufactured to ensure a controlled edge condition on the mating surface for less wear from sharp edges. The absence of lugs gives this style a low clearance but requires a tapered mandrel or cone for installation.
Spiral rings are free of sharp edges. They are the most difficult to install, usually via a tapered mandrel or cone, but they have the lowest clearance of the three style types. They are usually the best for tamper-proofing; choose an end type that makes them quite difficult to remove. Or, for easier removal, choose an end type that renders the spiral rings easy to remove with a flat-head screwdriver.
How do the costs and availability of retaining rings vary from style to style?
The cost and availability of each style of retaining ring may also play into your ultimate decision. The higher load and speed capabilities of a tapered section retaining ring are balanced by its somewhat higher cost. Constant section rings can be a lower cost way to meet the performance requirements of a variety of applications.
Spiral rings are coiled from flat-wire, so their manufacture requires less tooling than stamped parts. That makes it much faster and more cost effective to create spiral rings with custom sizes and shapes compared to other retaining ring styles.
How can I ensure I am choosing the right retaining ring for my application?
Your application requirements, installation practices, and budget are all factors to consider when choosing a retaining ring style. For a balanced review of your options, consider a manufacturer, like Rotor Clip, which supplies a range of retaining ring styles. Visit Rotor Clip’s website or schedule a consultation with its engineers to get help choosing the best retaining ring for your application.